Contents:
- Expert Assisted Services
- What Does the Gearing Ratio Say About Risk?
- Capital gearing ratio
- Meaning of highly geared in English
Wilko tries Improve Cash Flow by Moving to Monthly Rent Payments

Potentially pay less income tax – interest and other costs of gearing may be tax deductible, and could potentially reduce taxable income. Such costs are generally tax deductible if the borrowed money is used to invest in an income producing investment. Though there are several variations, the most common ratio measures how much a company is funded by debt versus how much is financed by equity, often called the net gearing ratio. A high gearing ratio means the company has a larger proportion of debt versus equity.
This is likely to increase the required returns of shareholders and may mean that debt lenders demand higher returns than are being paid on the current loans. The only possible limitation of the capital gearing ratio is this – this ratio is not the only ratio you should look at whenever you think of investing in a company. Let’s say you are looking at the capital structure of Company A. Company A has 40% common stock and 60% borrowed funds in the year 2016. Now you judge that Company A would be a risky investment because it is highly geared. But to get a big picture, you need to look beyond one or two years of data. You need to look at the last decade of the company’s capital structure and then see whether Company A has been maintaining high gear for a longer period.
But if it’s not the scenario and they have borrowed some debt for their immediate need, you can think about investment . The degree of gearing, whether low or high, reveals the level of financial risk that a company faces. A highly geared company is more susceptible to economic downturns and faces a greater risk of default and financial failure.
It is important to remember that although companies with higher gearing ratios generally carry more risk, high financial leverage does not necessarily indicate financial distress. While excessive debt can lead to financial difficulties and companies with low gearing ratios are generally considered more financially sound, the use of debt financing does not automatically raise a red flag. Low gearing/leverage ratio represents a low proportion of debt to equity and indicates lower financial risk. High gearing/leverage ratio represents a high proportion of debt to equity and indicates higher financial risk. Other companies who lack access to the stock exchange find it more difficult to raise equity finance and may need to turn to venture capitalists if they require equity finance. High level of required funding relative to the size of the firm – could be perceived by potential investors as increasing business risk even though the expansion is in the same industry.
Expert Assisted Services
Hence they charge a higher interest rate on longer-term lending than on short-term lending. However, short-term borrowing has a major disadvantage – renewal risk. Short-term loans have to be regularly renewed and the company carries the risk that lenders may refuse to extend further credit.
- Hence, it would not be considered incorrect to say that the debt-to-equity ratio is considered a gearing ratio category.
- There is a significant decrease in the “Value of the Firm” due to firm’s over-leveraging.
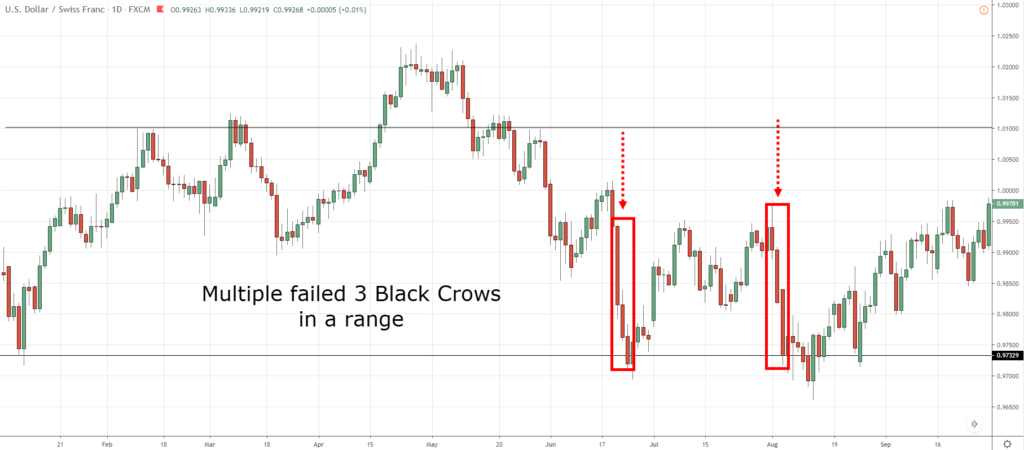
- But if its main competitor shows a 70% gearing ratio, against an industry average of 80%, the company with a 60% ratio is, by comparison, performing optimally.
- The capital structure should be determined within the debt capacity of the company and this capacity should not be exceeded.
This dominatesthe cheapness of the extra debt so the WACC starts to rise as gearingincreases. Also known as the intuitive view, the traditional view has notheoretical basis but common sense. It concludes that a firm should havean optimal level of gearing, where WACC is minimised, BUT it does nottell us where that optimal point is. The only way of finding the optimalpoint is by trial and error. So increasing gearing increases the cost of equity and that would increase WACC. The following diagram summarises the main practical factors whichmust be considered when choosing between debt and equity finance.
What Does the Gearing Ratio Say About Risk?
Conversely, a company that never borrows might be missing out on an opportunity to grow their business by not taking advantage of a cheap form of financing, if interest rates are low. A gearing ratio is a general classification describing a financial ratio that compares some form of ownerequity to funds borrowed by the company. Gearing is a measurement of a company’s financial leverage, and the gearing ratio is one of the most popular methods of evaluating a company’s financial fitness.
the firm is considered to be highly geared if Ratios are metrics, and to calculate gearing ratios, different aspects of the company are included. Highly geared businesses will have a debt to equity ratio of higher than 100%. Highly geared.Means having long-term fixed interest debt of over 50% of capital employed. This means a firm must spend large sums simply paying interest on loans. Capital structure of any firm is made up of Equity, Long Debt and Preference shares.
Capital gearing ratio
Proportion of equity share capital in relation to the total capital comprising the other securities is small leading to capitalization being highly geared. The cost of equity is equal to capitalization rate of pure equity stream plus a premium for financial risk. Any change in the leverage will not lead to any change in the total value of the firm and the market price of shares, as the overall cost of capital is independent of the degree of leverage.
The increase in Ke does not offset the benefit of the cheaper debt finance and therefore the WACC falls as gearing is increased. There may be restrictions imposed on the level of gearing, eitherby the company’s Articles of Association , or by previous loanagreements. Debt is usually cheaper than equity due to lower risk faced by theproviders of finance and the tax relief possible on interest payments.However, some debt, such as an unsecured overdraft, may be moreexpensive than equity. The issuers of the products named on this website can be found in the relevant disclosure document.
Wilko tries Improve Cash Flow by Moving to Monthly Rent Payments
Margin loans are a type of investment loan and have similar risks and benefits as other gearing strategies, however they also have some unique features. Home gearing involves using a property as security for an investment loan. Like all gearing strategies, both the benefits and risks must be considered.
Turmoil at ‘Chief’ Raises the Question: Is Empowering Corporate … – The New York Times
Turmoil at ‘Chief’ Raises the Question: Is Empowering Corporate ….
Posted: Tue, 28 Mar 2023 09:00:25 GMT [source]
Invest for the long term – this may give time to ride out any downturns in the market and take advantage of the upturns. Here is a list of some of the general benefits and risks of gearing as well as the steps to take to manage the risks involved. This equates to a greater amount of power transferred to the wheels. Installing 4.10 gears improves the car’s performance on the track but with negligible effects to the highway driving. If your car is equipped with an overdrive, you may not even notice a difference in gas mileage with the new higher gearing. ClearTax offers taxation & financial solutions to individuals, businesses, organizations & chartered accountants in India.
On the other hand, if the firm has more common equity, the investors’ interest would be taken care of. When sourcing for new capital to support the company’s operations, a business enjoys the option of choosing between debt and equity capital. Most owners prefer debt capital over equity, since issuing more stocks will dilute their ownership stake in the company. A profitable company can use borrowed funds to generate more revenues and use the returns to service the debt, without affecting the ownership structure.
Meaning of highly geared in English
Expansion of the https://1investing.in/ takes place by issuance of short term and marketable securities. The fixed interest cost of the firm increases thereby increasing its risk. Incorporate debt in its capital structure to a greater extent.
A higher financial leverage ratio indicates that a company is using debt to finance its assets and operations — often a telltale sign of a business that could be a risky bet for potential investors. The gearing ratio shows how encumbered a company is with debt. Depending on the industry, a gearing ratio of 15% might be considered prudent, while anything over 100% would certainly be considered risky or ‘highly geared’. Company ABC wants to fund its expansion, but cannot sell additional shares to investors at a reasonable price. If Company ABC has equity worth Rs.20 lakh, the debt-to-equity ratio is 5, i.e.
West Virginia leaders promote Mountain State on ‘ChooseWV’ tours – WV News
West Virginia leaders promote Mountain State on ‘ChooseWV’ tours.
Posted: Tue, 28 Mar 2023 15:24:00 GMT [source]
Gearing ratios are useful for both internal and external parties. Financial institutions use gearing ratio calculations when deciding whether to issue loans. In addition, loan agreements may require companies to operate with specified guidelines regarding acceptable gearing ratio calculations. Alternatively, internal management uses gearing ratios to analyze future cash flows and leverage. The firm with low business risk can be able to carry high levels of gearing, since its stability can enable the firm to withstand to high levels of financial risk. In the initial stages of financing with lower levels of debt, the firm’s distributable profits are reduced by the interest payments.
Now let’s look at the formula to calculate the ratio all by ourselves to understand the nitty-gritty of a firm’s capital structure. Capital structure is the particular combination of debt and equity used by a company to funds its ongoing operations and continue to grow. Gearing can be thought of as leverage, where it’s measured by various leverage ratios, such as the debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio. Most leveraged and inverse funds, also called “geared” funds, aim to provide a multiple of the return of an index or other benchmark for a single day, before fees and expenses.
Something between 25% – 50% would be considered normal for a well-established business which is happy to finance its activities using debt. A gearing ratio of more than 60% is considered to reflect high dependency of a company on external capital to finance its investments and operations. If the same business used $2.5 million of its own money and $2.5 million of borrowed cash to buy the same piece of real estate, the company is using financial leverage.
